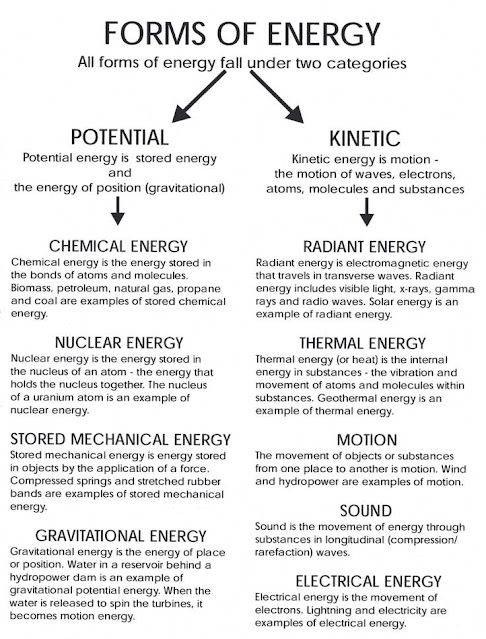
Here's an overview of the various forms of energy and their characteristics:
Potential Energy:
Definition: Stored energy based on an object's position or configuration.
Example: Gravitational potential energy, such as water stored in a reservoir behind a dam.
Kinetic Energy:
Definition: The energy of motion, which includes the movement of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances.
Example: A moving car or a flowing river.
Chemical Energy:
Definition: Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is released during chemical reactions.
Example: Energy stored in biomass, petroleum, natural gas, propane, and coal.
Radiant Energy:
Definition: Electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. It includes various types of electromagnetic radiation.
Example: Solar energy, visible light, x-rays, gamma rays, and radio waves.
Nuclear Energy:
Definition: Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. It is the energy that holds the nucleus together.
Example: Energy from nuclear reactions in uranium atoms.
Thermal Energy:
Definition: Internal energy within substances due to the vibration and movement of atoms and molecules.
Example: Geothermal energy and heat from a stove.
Stored Mechanical Energy:
Definition: Energy stored in objects due to the application of a force.
Example: Energy stored in a compressed spring or a stretched rubber band.
Motion:
Definition: The energy resulting from the movement of objects or substances from one place to another.
Example: Wind energy and hydropower.
Sound:
Definition: The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves, characterized by compression and rarefaction.
Example: The sound produced by a ringing bell or a musical instrument.
Gravitational Energy:
Definition: The energy associated with an object's position in a gravitational field.
Example: Water stored at height behind a dam, which can be converted to motion energy when released.
Electrical Energy:
Definition: Energy due to the movement of electrons through a conductor.
Example: Electricity powering devices and lightning.
Each form of energy plays a crucial role in different contexts, and understanding them helps in harnessing and utilizing energy effectively in various applications.